- Anatomy (body structure): the science of studying the composition reply form or the body and known to science explained dg
- Physiology (body physiology): yg studying physiological sciences (function) part of the tool or tissue
- Anatomical position: standing upright, arms at your sides, palms facing forward.
- Medial field: dividing the body into 2 parts left and right.
- Frontal field: dividing the body into 2 parts ie front (anterior) and rear (posterior)
- Transverse field: divides the body into 2 parts namely the (superior) and bottom (inferior)
Anatomical Position
Imagination Field Body Dividers
- Proximal: close to the reference point / axis of the body
- Distal: away from the reference point / axis of the body
- Head: skull, face and lower jaw
- Neck
- Trunk body: chest, abdomen, back and pelvis
- Members of motion for: shoulder joint, upper arm, forearm, elbow, wrist and hand
- Lower limbs: hip joint, leg up (thigh), knee, lower leg, ankle and foot.
Body Cavity
Division of Abdominal Cavity
- The human body is composed of: the cell network --- --- --- organ system
- System in the human body:
- System framework
- Muscular system / muscular
- Respiratory System / Respiratory
- Circulatory system / circulation
- The nervous system / nerve
- Digestive system / digestive
- System clogged glands / endocrine
- Urinary System / Urinary
- Skin
- Sensory
- Reproductive System
- System framework: classification of bone: long bone / pipe, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid
- Division order system:
- bone head
- order chest
- spine and pelvis
- limb bones of
- lower limb bones
- Composition of the framework:
- Skull brain: composed of the brain, skull base
- The skull's face: the nose, jaw, tongue tl
- Spine: neck, back, hips, crotch and topsy-turvy
- Framework of the chest: sternum and ribs
- Pelvic bone: bone intestines, and pubic bone tuberosities
- Members of motion of: clavicle, scapula, radius, ulna, a bone lever, tanagan wrist bone, tl palms and finger bones.
- Lower limb: thigh bone, knee bone, shin, ankle bones, foot bones and toe bones.
- The framework:
- Supporting body
- Protects organs
- Places attached muscles and body movement
- Gives the body shape of the building
- Muscle systems: yg enables the body organs can be moved
- Classified into:
- Skeletal muscle / shift latitude / striated
- Smooth muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Skeletal muscle: a self-moving equipment and maintain an active posture, moved on the orders of the brain, in a state of rest remains a tension / muscle tone
- Composition of skeletal muscle: the muscles of the head, neck, shoulders, chest, abdomen, back, base of upper arm, lower arm around the pelvis, upper and lower limbs
- Muscle tone functions:
- Maintaining the attitude and position of the body
- Cavity changes by holding the abdominal muscles
- Keep blood pressure by the muscles of the blood vessel wall
- Smooth muscle: injure the body of work without realizing it, ill-based command but by stimulating the brain, the body structure diyemukan shaped tubuler spt yg gastrointestinal tract, urinary system, blood vessels, respiratory tract in the lungs
- Cardiac muscle: a blend of smooth muscle and striated muscle, has its own electrical system, can set their own pace and without the command frequency of the brain
Muscle System
- Respiratory system is divided into 2:
- Breathing in (gas exchange in the network)
- External respiration (gas exchange in the lungs)
- Composition:
- Airways of: mouth, nose and farings
- Lower respiratory tract: the base, stem and bronchus
- Lung
- Respiratory muscles: chest diaphragm, chest wall muscles, muscle ventilator.
- Alveoli (where gas exchange)
- The brain (the central respiratory regulation
Respiratory System
- Respiratory Function:
- Taking oxygen
- Removing carbon dioxide
- Warms and moisturizes the air
- The process of breathing:
- Inhale / inspiration / ekshalasi
- Exhale / expiratory / ekshalasi
- 4-6 minutes of oxygen will cause brain damage
- Usually 8-10 minutes will menyebabakan brain cell death
- How to breathing: respiratory chest and abdomen
Breathing Process
- Blood circulation system:
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood and its components
- Lymph channels
- heart: a muscular organ dg berbentu cone peak below and above the base, between the 2 lungs, chest tl behind, facing to the left and work autonomously
- Blood vessels:
- Pulse of blood vessels / arteries
- Veins / venous
- Hair vascular / capillary
Circulatory System
Heart
Blood Vessels
- Capillary has a function:
- Interface arteries and veins
- Place of substance exchange between blood and tissue fluid
- Taking the results of the gland
- Absorb the nutrients in the gut
- Kidneys filter the blood in
- Lymph channels: soft tissue is very small capillaries in the tissues of organs, collecting, sorting and distributing the lymph fluid into the blood to clear the network
- The function of blood;
- Transporter: oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrient substances and substances are not useful
- Immune disease
- Mengedarakan heat throughout the body
- Helps blood clot when there is injury
- Composition of blood:
- Water
- Protein
- Mineral
- Organic materials
- The amount of blood in the body: ± 1 / 13 x BB or 8%
- Blood consists of:
- Liquid plasma in which dissolved nutrients, waste and immune substances
- Red blood cells: ± 5 million / mm ³
- White blood cells (5000-10.000/mm ³)
- Platelets (200.000-400.000/mm ³)
- Factors affecting circulation reply:
- Contents and blood components
- Pressure and blood vessels
- Heart conditions and blood vessels
- Circulation consists of: a small circulation and a large
- Pulse; every heart beat it will be forwarded through the arteries
- Nervous system: the organ reply, and working to coordinate with the body kejasama
- The division of the nervous system:
- Central nervous system:
a. Brain: the cerebrum, brain stem small and
b. Spinal tube
b. Spinal tube
a. Somatic nervous system
b. Autonomic nervous system: sympathetic and parasympathetic
b. Autonomic nervous system: sympathetic and parasympathetic
- Function:
a. Sensory (received ransang)
b. Motor: regulate movement, other systems, consciousness, language and emotion
b. Motor: regulate movement, other systems, consciousness, language and emotion
Brain
Spinal Nerve
- Digestive system: the channel receiving food from outside for absorbed thereby help digest dg caie enzymes and substances from the mouth to the anus
- Composition:
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine: gut 12 fingers, jejenum and ileum
- Large intestine: seikum, ascending colon, appendix, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, intestine and rectum axis
Gastrointestinal Composition
- Sap digestive organs:
- Salivary gland
- Gastric lymph
- Gland liver
- Pancreatic gland
- Intestinal lymph
- Function: process becomes makann posterior nutrients are absorbed into the blood, every part of the digestive arrangement has funsi each for helping the process of respiration
- Endocrine system: glands clogged / adalh endocrine gland secretory hasi wrote submit to blood dala in glandular tissue without passing through the channel and the result is called hormone sekrersinya
- Endocrine organs:
- Gland hipofise
- Thyroid and parathyroid glands
- Suprarenal gland
- Thymus gland
- Gland pinealis
- Gonad
- Endocrine system function
- Generate tissue for hormones
- Control the body's glands work
- Stimulate the body's glands work
- Merangsng tissue growth
- Regulate metabolism, oxidation, and increased absorption in the small intestine glukiosa
- Affect the metabolism of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and water
- Effect of deficiency or excess production will cause endocrine diseases
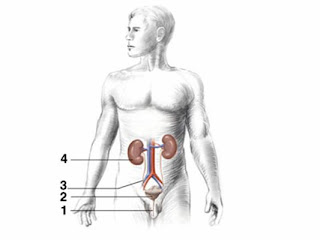
- Urinary system: the blood screening process to absorb the reply is used to free the body and substance are not used body reply
- Composition:
- Kidneys: urinary issue, attached directly to the rear wall of the stomach waist-high segment of the third bone in the left and right
- Ureter
- Bladder
- urethra
- Renal function:
- Excrete toxins
- Regulate fluid balance
- Adjust the salt concentration of the blood
- Regulate blood acid base
- Removing the remaining metabolism: ammonia, creatinine
Composition of Urinary System
- Skin: network layer on the outside, cover and protect the surface of the body, mucous membranes associated reply cavities covering the entrance hole
- Composition:
- Cuticle layer
- Skin layer hides
- Subcutaneous layer
- Functions of skin:
- Preventing injury
- Protection against microorganisms
- Maintaining body temperature
- Regulate fluid balance
- Tools stimulation from the outside
- Sensory organs: around, pressure, temperature and pain
Skin Structure
- Five senses: an organ for receiving types of stimulation (stimulus) a particular skin layer
- Sight (eye) is composed of:
- Aids eye: cavity of the eye, eyebrows, eyelids, tear glands, eye muscle
- Eyeball
- Function: sight as acceptor stimulation of rays on the retina through the optic nerve fibers to the visual centers in the brain to interpret.
Eyes
Eye Pupil
- Sense of hearing (ears) are composed:
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear
- Function as a process of hearing and balance
- Sense of smell (nose): a tool of smell located in the nasal cavity, out of the olfactory nerve endings. These nerve fibers appeared at the top of the mucous membranes professed as olfactory bulbus. The smell of the nasal cavity entrant will stimulate the olfactory nerves, stimulating forwarded to the central olfactory
- Sense of taste (tongue): as the senses of taste, is located on the floor of the mouth is covered by mucous membrane and move in any direction. Mucous membranes and pharynx contains nipple nipple-buds.
- Composition: the base of the tongue, back of the tongue and the tip of the tongue.
- Function:
- Feel the sense of food.
- Refles tool, with the sense to stimulate the digestive sap out
- Kinds of taste: bitter at the base of the tongue, sweet tip of the tongue, salty on the tip & side of the tongue, sour on the side of the tongue
- Reproductive system: the reproductive organs to form the genital tract associated with Urinary tract. On the second man this tract is directly related to women are not united.
- Composition tool male genitalia:
- Glands: testes, seminal vesika, prostate, bulbouretralis
- Gland duktuli: epididymis, seminal duct, urethra
- Wake connector: scrotum, penis fenikulus spermatikus
- Composition means female genitalia:
- External genitalia Tools: tundun, big lips, small lips, klentit, porch, hymen and perineum
- Tools genitalia in: liang genitalia, uterus and ovaries
- Function:
- Reproductive organs
- Testes produce sperm
- Ovaries produce ova
- These organs also produce hormones reply form male and female
Female Reproductive Organ
Male Reproductive Organ